PVA High Strength & Modulus Fiber
PVA high - strength & high - modulus fiber taking polyvinyl alcohol as its major raw materials is produced by a special process. It is of high strength, high modulus, acidproof, alkaliproof, abrasion resistance and sunlight resistance which are possessed by PVA fiber, thus it is much better than the other products in general. With these excellent properties, it has a wide application in industry fabric, building reinforcing materials, package materials, ropes and meshes .
•
Concrete reinforcing materials used for buildings.• Ideal replacement of asbestos and glass fiber.
• Reinforcing materials for upholstery.
• High strength fishing meshes, cables, safety nets.
• High strength fabric used in industry.
• Modern package reinforcing materials.
|
Item
Property |
High strength & modulus Ⅰ . |
High strength & modulus Ⅱ . |
Super-short staple fiber Ⅰ. for buildingmaterials |
Super-short staple fiber Ⅱ. for building materials |
|
Density (g/cm2) |
1.26 |
1.26 |
1.26 |
1.26 |
|
Titre (dtex) |
2.0 _0.3 |
2.0 _0.3 |
1.7 - 3.0 |
1.7 - 3.0 |
|
Length (mm) |
2 - 65 |
2 - 65 |
2 - 65 |
2 - 65 |
|
Tenacity (CN/dtex) |
> 10.5 |
> 10.5 |
≥ 8 |
≥ 6 |
|
Modulus (CN/dtex) |
> 240 |
> 240 |
>200 |
>150 |
|
Breaking elongation (%) |
< 7 _1.5 |
<7 _1.5 |
|
|
|
Reduction in hot water |
< 2 |
< 3 |
|
|
|
Acid proof |
Good |
good |
good |
good |
|
Alkali resistance |
Good |
good |
good |
good |
|
Ultraviolet resistance |
Good |
good |
good |
good |
|
Electric conductivity |
Low |
low |
low |
low |
|
Thermal conductivity |
Low |
low |
low |
low |
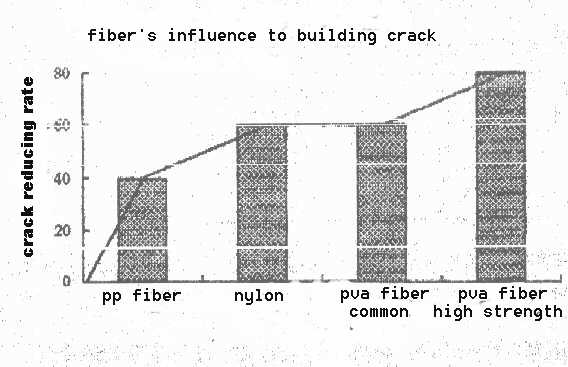
C. Fiber breaking elongation comparisons
| Fiber |
Vinylon (high strength) |
Vinylon (usual) |
Nylon |
PP fiber |
Polyester (usual) |
Polyester (high strength) |
|
Breaking elongation % |
7 |
15 |
20 - 40 |
15 - 35 |
14 - 25 |
10 - 14 |
D. Alkali resistance comparisons:
| Test condition |
Fiber strength loss ratio (%) |
||||||
|
Density % |
Temperature ℃ |
Duration time (hr) |
Vinylon-high strength |
Viscose fiber yarn |
Nylon 6 |
Polyester |
|
|
1 |
20 |
10 |
0 |
12 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
100 |
100 |
7 |
29 |
25 |
71 |
|
|
40 |
20 |
10 |
0 |
100 |
18 |
4 |
|
| Exposed in the sunshine(hour) |
Fiber strength loss ratio ( % ) |
|||
|
High strength vinylon |
Nylon 6 |
Viscose fiber |
Cotton |
|
|
100 |
3.05 |
19.6 |
4.26 |
3.67 |
|
300 |
7.93 |
41.2 |
7.45 |
30.73 |
|
500 |
10.98 |
65.09 |
25.00 |
38.53 |
|
700 |
11.16 |
74.51 |
63.30 |
49.54 |
F. Applications in asbestos cement products of PVA high strength & modulus fiber:
Shortcomings of the main reinforcing materials:
•
As a reinforcing material, asbestos has a small tenacity and is easy to break.• It has the property of acid resistant but not alkali proof.
AN IDEAL REPLACEMENT OF ASBESTOS AND GLASS FIBER:
Advantages:
•
Good physical and chemical properties.• Excellent mechanics properties to improve board’ toughness and anti-
shock ability and to reduce break rate.
• With adequate supply , good quality and good dispersing properties.
• Being suitable for all types of cement with good alkali & acid resistant properties.
• Raising the board’s anti-crook temperature and reducing the product volume.
• Improving the circumstances.
• No need to change original equipment.
| Unit |
Cement |
Asbestos |
Vinylon |
Paper pulp |
Sepiolite |
Additive agent |
Ratio of the replacement by asbestos |
Quantity of the replacement by asbestos |
|||
|
KG |
250 |
26 |
4.7 |
6 |
proper amount |
proper amount |
1: 4.5 |
- |
|||
|
% |
87.2 |
9.1 |
1.64 |
2.1 |
- |
- |
- |
40 |
|||
2) Cement plate
| Unit |
Cement |
Asbestos |
Vinylon |
Sepiolite |
Paper pulp |
Quantity of replace asbestos |
|
KG |
250 |
15 |
4.7 |
30 |
6 |
- |
|
% |
81.78 |
4.91 |
1.54 |
9.81 |
1.96 |
70 |
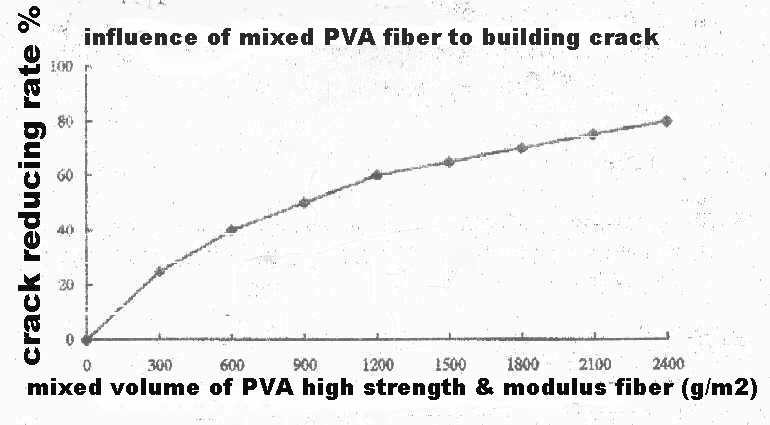
H. Applications in building concrete of PVA high strength & high modulus fiber:
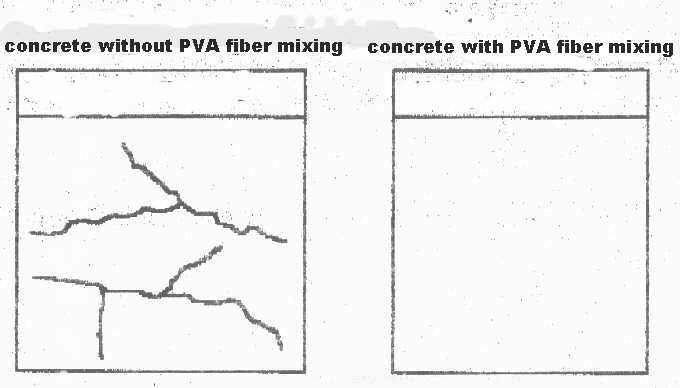
In the concrete industry, the only reason for tortoise-cracking is that the inner stress to the concrete surpasses the strength it can bear. People have tried to reinforce the structural strength of the concrete products to offset the stress from outside, but they can’t control it effectively, for quite a long time, due to the inner stress caused by shrinkage. During the period of molding, the tortoise-cracking forms within 24 hours after it is molded because of the shrinkage caused by the dryness inside the concrete.
Mixing PVA high strength & high modulus fiber into the primary or secondary reinforcing materials can improve the building material's anti-draw ability and toughness, increase the concrete’s ability of tension resistance, reduce the water loss rate, improve the concrete material’s ability of anti-breaking and reduce effectively tortoise-cracking. Thus it is an ideal reinforcing material in the building industry.
•
Prevent the tortoise-cracking.• Increasing the tenacity, anti-breaking ability and abrasion resistance.
• Raising the weary resistance of anti-elasticity.
• Reducing the water osmosis.
• Extending the life cycle of the concrete.
•
With good dispersing ability, it can be dispersed uniformly in every part of the product.• It is suitable for concrete which can’t have metal in it.
• It does not corrode and does not have chemical reactions.
• With excellent ability of anti-alkali, it is suitable for any type of the cement.
• It doesn’t affect the surface property of the concrete.
• It can decrease the labor strength and improve the working environment.
• It is easy and safe to use without any need to add any equipment.
I. SUGGESTED MIXING QUANTITY:
|
|
|
|
|
|
****************************************
Huiling Information Consulting Co.Ltd.
Email:
webmaster@chinafiber.com
Agent in Europe:
Tel: +49 2365 5175 0, Fax: +49 2365 5175 20
E-Mail:
Sossna@sossna.de